Aluminum veneer stands out as a remarkably versatile and popular choice. Often seen adorning the facades of modern buildings, enhancing interior spaces, and contributing to innovative designs, aluminum veneer offers a unique blend of strength, lightweight properties, and design flexibility. If you’ve ever wondered about the sleek, metallic surfaces that define many modern structures, chances are you’ve encountered aluminum veneer.
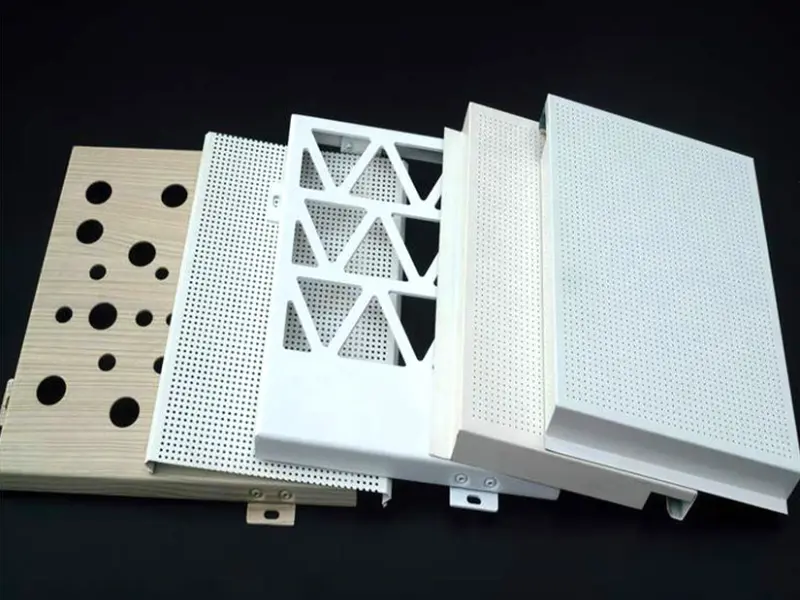



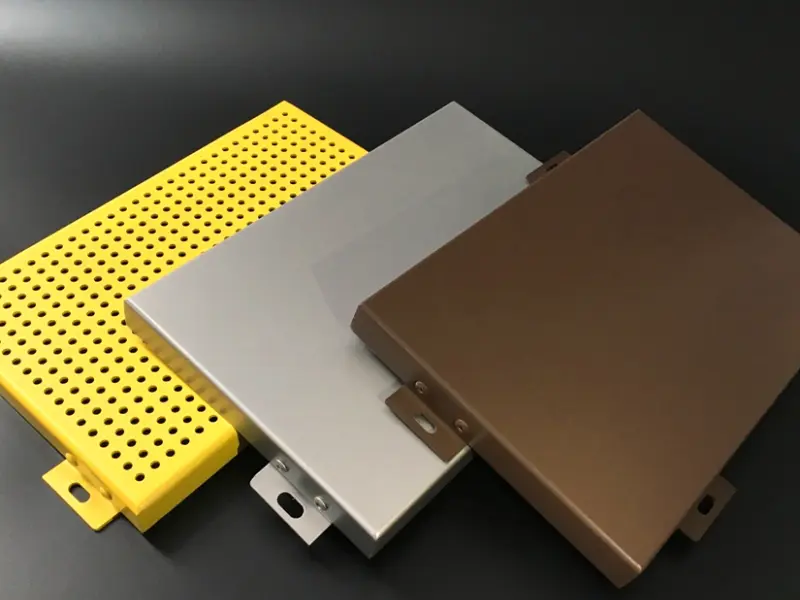
Key Features and Benefits of Aluminum Veneer
Choosing aluminum veneer for a project offers a wide range of advantages that appeal to architects, builders, and property owners alike. Its inherent properties make it an excellent choice for modern construction.
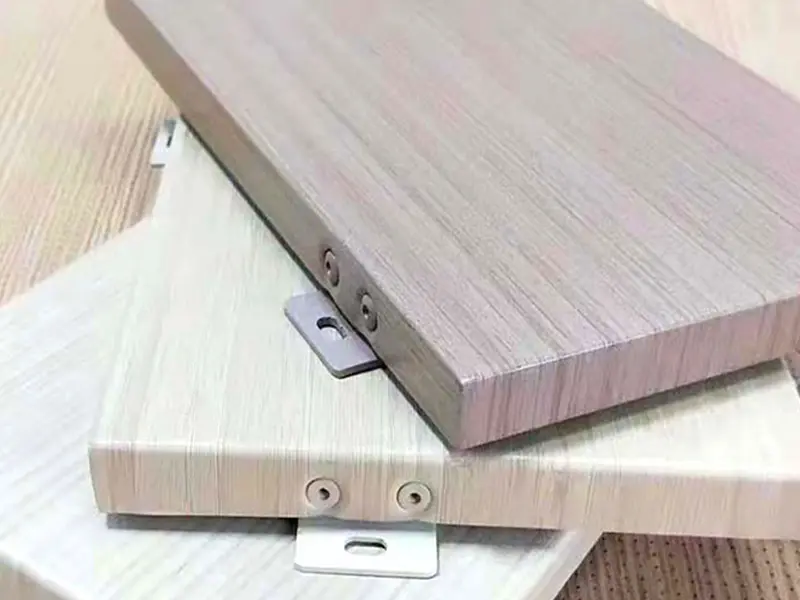


| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Lightweight Durability | Easy handling, reduced structural load, cost savings. |
| Exceptional Weather Resistance | Resists corrosion, rust, UV, rain, and extreme temperatures; long lifespan. |
| Superior Fire Resistance | Non-combustible, significantly enhances building fire safety. |
| Design Flexibility | Easily shaped into curves, custom forms, and perforations. |
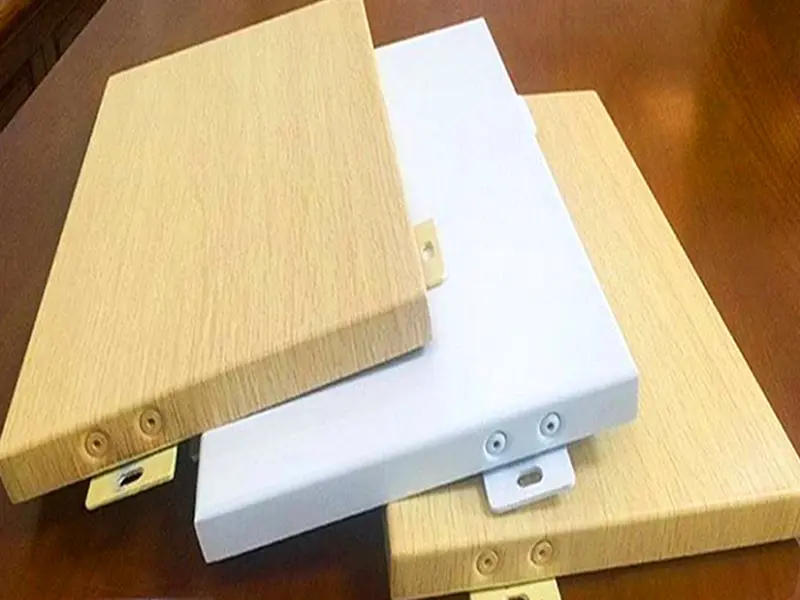
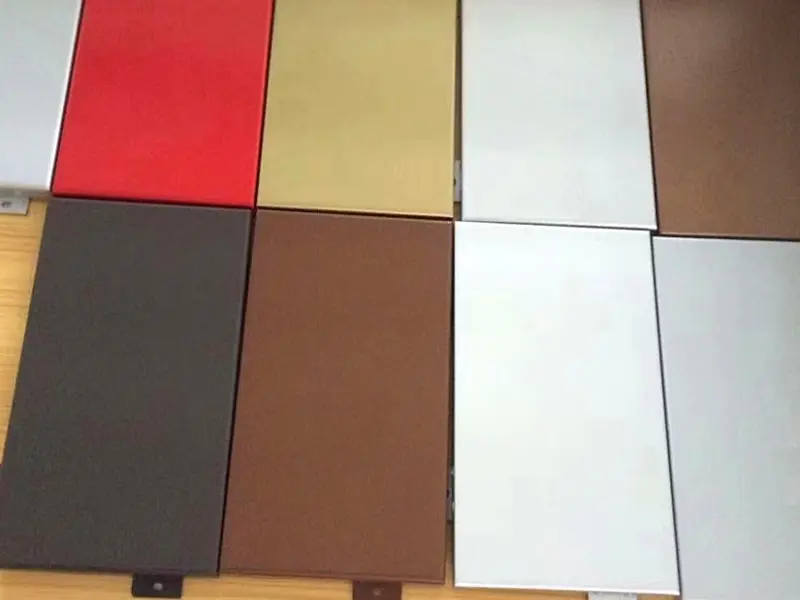
| Wide Range of Finishes | Extensive colors and textures (PVDF, powder coating) for perfect aesthetics. |
| Easy Maintenance | Smooth, coated surface is simple to clean, retains appearance. |
| Sustainable & Recyclable | 100% recyclable, an environmentally friendly building material. |
| Impact Resistance | Offers good protection against minor impacts. |
Applications of Aluminum Veneer
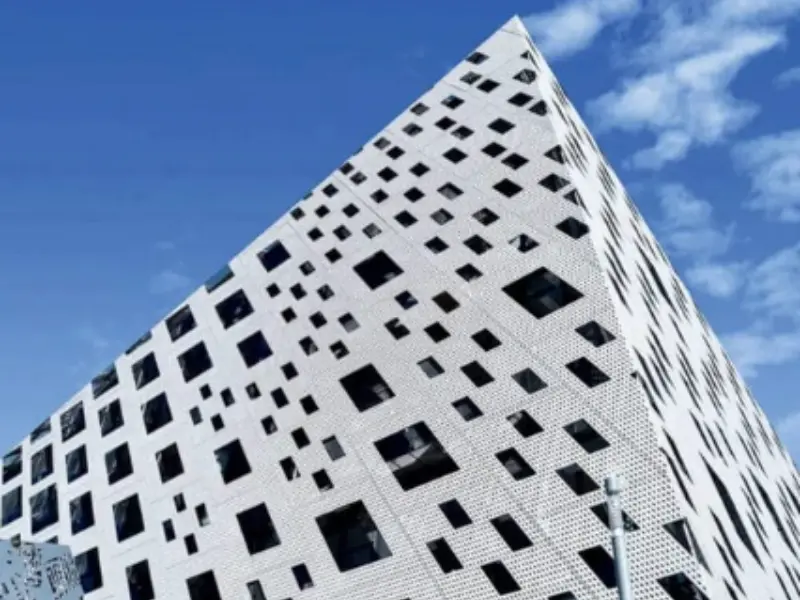

The versatility and performance characteristics of aluminum veneer make it suitable for a broad spectrum of architectural and design applications. Its use is prevalent in both new constructions and renovation projects.
- Building Facades & Exterior Wall Cladding: Modern, sleek finish for various building types.
- Column Covers: Encasing structural columns for protection and aesthetic appeal.
- Ceilings & Soffits: Lightweight and attractive for large overhead areas.
- Canopies & Awnings: Weather-resistant for outdoor protective structures.
- Decorative Interior Walls: Contemporary and durable finishes in lobbies, corridors.
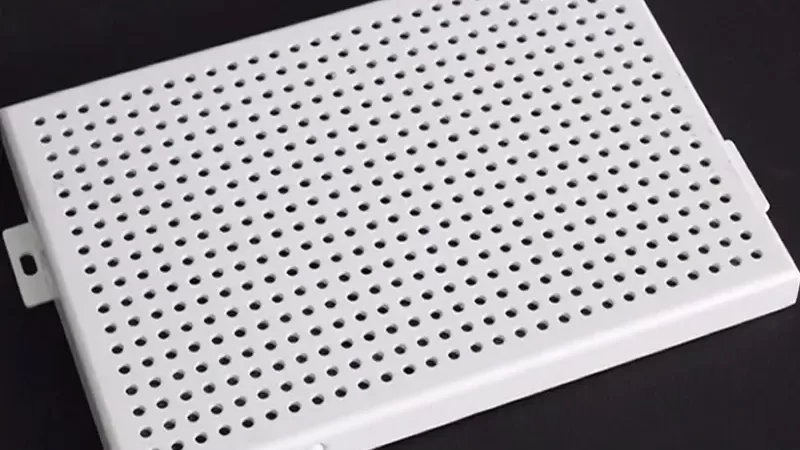
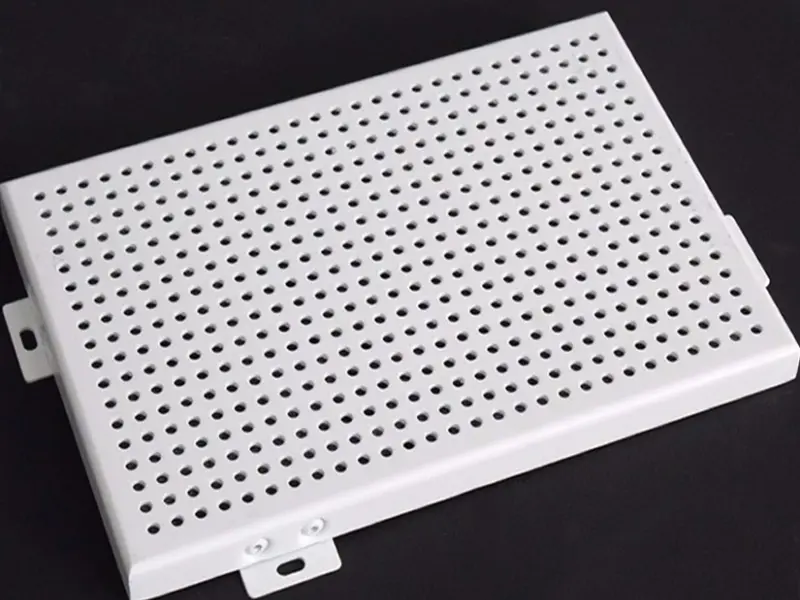
- Perforated Panels: Artistic patterns, ventilation, light diffusion elements.
- Balustrades & Railings: Combining safety with modern design.
- Signage Backings: Durable base for outdoor and indoor signs.
- Specialty Architectural Features: Unique elements requiring custom metal finishes.
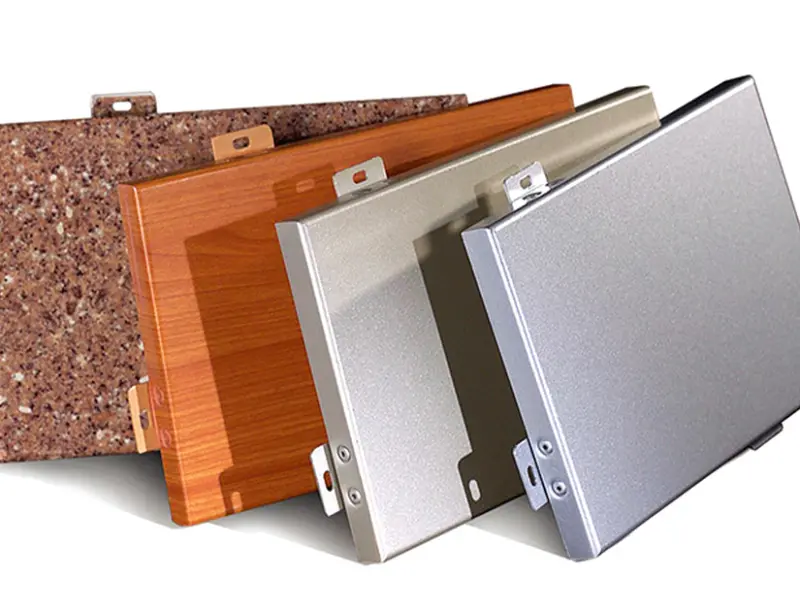
Types and Specifications of Aluminum Veneer
Aluminum veneer panels come in various forms and can be customized extensively to meet project-specific demands. Here’s a breakdown of common types and specifications:
Material Alloys
The choice of alloy impacts the panel’s strength and workability.
| Alloy Series | Primary Composition | Key Characteristics | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1100 Series | Pure Aluminum | Good workability, excellent corrosion resistance. | Interior, simpler forms |
| 3003 Series | Aluminum-Manganese | Stronger than 1100, better corrosion resistance. | Most common for exterior facades |
Panel Thickness Options
Thickness is crucial for rigidity, durability, and load-bearing capacity.
| Thickness (mm) | Thickness (in) | Rigidity Level | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 0.06 | Standard | Interior, small exterior features |
| 2.0 | 0.08 | Good | Common for exterior facades, medium panels |
| 2.5 | 0.10 | Enhanced | Larger panels, areas with higher wind loads |
| 3.0 | 0.12 | Maximum | Heaviest duty, complex shapes, high wind/impact zones |
Common Surface Coating Types
The coating provides color, texture, and protection.
| Coating Type | Key Performance | Aesthetic |
|---|---|---|
| PVDF (Fluorocarbon) | Excellent weather, UV, corrosion resistance; long-lasting. | Wide range of colors, metallic, high-performance. |
| Powder Coating | Durable, good scratch resistance, wide color selection. | Uniform solid colors, often more economical. |
| Anodizing | Hard, protective oxide layer, abrasion resistance. | Translucent metallic hues, natural aluminum look. |
Typical Panel Forms & Customization
Aluminum veneer can be fabricated into diverse shapes.
| Panel Form | Description | Customization Capability |
|---|---|---|
| Flat Panels | Simple, planar sheets. | Any desired rectangular/square dimensions. |
| Curved Panels | Formed with specific radii. | Custom radii and arcs for unique architectural curves. |
| Perforated Panels | Sheets with precision-cut holes in patterns. | Custom hole sizes, shapes, and patterns (CNC). |
| Column Covers | Semi-circular or multi-faceted to wrap columns. | Matched precisely to column diameter and height. |
| Cassette Panels | Panels with folded edges designed for interlocking systems. | Custom dimensions for specific facade grid systems. |
PVDF Coating Specifications (Example for High Performance)
PVDF is highly valued for its long-term exterior performance.
| PVDF Layer Count | Coating Thickness (µm) | Key Benefit | Estimated Durability |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Coat | ≥25 | Good weather resistance, color retention. | 10-15 years |
| 3-Coat | ≥35 | Excellent UV, weather, and corrosion resistance. | 15-20 years |
| 4-Coat | ≥45 | Superior protection for extreme environments. | 20+ years |
Why Choose Aluminum Veneer for Your Next Project?
The decision to use aluminum veneer is often driven by its compelling combination of aesthetic appeal, functional performance, and long-term value. For architects, it offers boundless creative freedom. For developers, it means a durable, low-maintenance, and attractive finish. For the environment, it represents a sustainable choice. Its inherent strength-to-weight ratio, fire safety, and ability to withstand the elements make it a smart investment for any building envelope or interior feature. As a versatile architectural aluminum solution, it provides both stunning visual impact and lasting integrity.
What Exactly is Aluminum Veneer?
At its core, aluminum veneer is a high-grade aluminum alloy sheet that has been processed to create a finished panel, typically used for cladding, decoration, and architectural applications. It’s not a composite material (like aluminum composite panel – ACP) but a solid piece of aluminum, making it a robust and single-layer solution.
The term “veneer” refers to its application as an outer layer or facing, giving a structure its visual appeal and a layer of protection. These panels are precisely cut, bent, welded, and surface-treated (often with painting or powder coating) to meet specific design requirements. The result is a lightweight, durable, and aesthetically pleasing panel that can dramatically transform the look and performance of a building.
